1. Testing, Testing…¶
You can find the video summary for this section here.
dbt Tests allow you to validate your data models in either:
Models
Freshness of data
and other items
There are two type of tests:
Built-in, default, schema tests: applied in the .yml file, returns the number of records that do not pass an assertion
Custom data tests
Our tests our configured in our dbt Repo in the dbt_project.yml configuration
test-paths: ["tests"]
The following is a visual example showing the default, custom, and path for our tests.
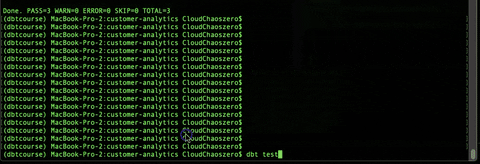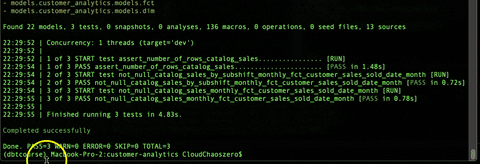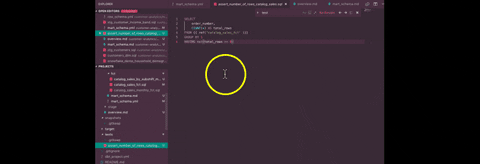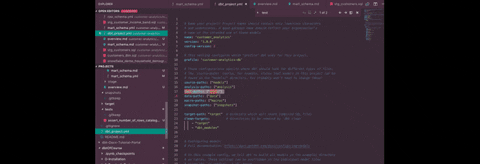
1.1. Default tests¶
The following is a great way to get started on dbt Tests:
https://docs.getdbt.com/tutorial/setting-up/
As an example, we work within the .yml files to create “schema tests”:
Using dbt test command, we test the following schema configurations:
-- mart_schema.yml
version: 2
models:
- name: some_table_name
columns:
- name: order_id
tests:
- unique
- not_null
- name: status
tests:
- accepted_values:
values: ['placed', 'shipped', 'completed', 'returned']
1.2. Custom Tests¶
Notice, there is a test/ folder in our repository. This is a place reserved for creating custom data tests outside of our built-in tests.
For example, let’s create a test assert_number_of_rows_catalog_sales.sql in the test folder
-- test/assert_number_of_rows_catalog_sales.sql
-- Count the total number of rows >= 0.
-- Therefore return records where this isn't true to make the test fail.
-- Note: This is an equivalent to yml confiug tests -not_null.
SELECT
order_number,
COUNT(*) AS total_rows
FROM {{ ref('catalog_sales_fct' )}}
GROUP BY 1
HAVING not(total_rows >= 0)
You can find so much more about dbt tests from the dbt team here.